What Is Purchase Order | Purchase Order Format

From elaborating what a purchase order format is to describing its process, this page has got it all! Read to know all about it.
A purchase order, also known as PO, is a commercial document and the first official offer which is issued by a buyer to a seller, indicating quantities, types, and agreed prices for services or products. It is used to control the purchasing of products and services from external suppliers.
What Is Purchase Order?
A purchase order, often known as a ‘PO’, is an official document issued by a buyer that commits to paying the seller for the sale of certain items or services to be supplied in the future.
The buyer benefits from the ability to make an order without having to pay right away. PO is a tool for a seller to extend credit to buyers without taking any risks because the buyer is required to pay once the items or services are delivered.
Each PO has a unique number that both the buyer and the seller may use to track delivery and payment. A blanket purchase order is a promise to buy things or services on a continuous basis, up to a particular limit.
Although purchase orders add a few more segments to the buying process, they serve to guarantee that the buyer and seller have a smoother transaction. They also serve to minimize the risk of completing an order that is incomplete or incorrect.
In a nutshell, these agreements allow the buyer to convey their demand to the seller in a simple and clear manner.
Furthermore, if the customer refuses to pay for a product or service after it is delivered, the seller is protected since the purchase order serves as a binding contract between the two parties. Or you can use a mobile CRM for creating a database of all your customers.
Finally, some commercial lenders will utilize purchase orders as a reference when lending money to a company.
How many types of Purchase Orders exist?
The following are the four main types of purchase orders:
Standard Purchase Orders
A standard purchase order is often used for procurement that is irregular, infrequent, or one-time. As previously said, it comprises a detailed description of the transaction, including the price, quantity, payment, and delivery schedules.
When to use a Standard Purchase Order?
- When there is a one-time request for products or services.
- The order’s details are available (delivery date, quantity, description, price.).
- If in a legal agreement, both parties are obligated to make the payment and send/receive the goods/services.
Planned Purchase Orders
A planned purchase order, like standard purchase order, is fairly detailed. The products and services to be acquired, as well as their costs need to be described in a planned purchase order.
It also includes payment and delivery dates, but they are viewed as estimates. Individual orders are placed when a release is issued against a planned purchase order.
When to use a Planned Purchase Order?
- The goods/services are expected in the future.
- For ongoing orders, suppliers and buyers are putting together a temporary agreement.
- Based on when the organization anticipates reaching the reorder point, there is a loosely defined delivery timetable.
Blanket Purchase Orders
A blanket purchase order is when a buyer agrees to buy specified items or services from a specific seller, but not in any definite amount. In a blanket purchase order, prices may or may not be confirmed.
This sort of order is often used to purchase a group of things from a provider on a regular basis, such as basic materials and supplies.
When to use a Blanket Purchase Order?
- The type of service or product required is known, but the amount and timing of the goods are unknown.
- A corporation predicts its demand for services or products over a certain period of time.
- The vendor and buyer have agreed on expenditure limits and other terms and conditions.
- To get a better deal under the secured contract, which will entail recurring purchases.
Contract Purchase Orders
A contract purchase order specifies the vendor’s information, as well as payment and delivery terms, if applicable. The items to be purchased are not mentioned.
A contract purchase order is used to establish a contract and terms of supply between a buyer and a seller as the foundation for a long-term business relationship.
When raising a standard purchase order to place an order for a product, the purchaser might refer to the contract purchase order. Companies use CPOs to form a contract with a vendor when they know they want to do business with them but have not yet concluded the transaction.
It establishes the parameters by which the transactional relationship will function in the future, including the SPOs that will be issued. CPOs are normally issued for a specific period of time and have an expiration date, which is commonly one year.
When to use a Contract Purchase Order?
- Between the supplier and the buyer, there is a formal long-term agreement.
- To establish legally enforceable terms and conditions for any future dealings.
- They serve as a foundation upon which SPOs can be created later.
- They are used to accelerate and secure the purchase transaction process between the two parties as they do not have an expiration date.

How do Purchase Orders work?
A purchase order must observe a specific step-by-step method termed the Purchase Order Process in order to simplify the procurement of products and services that an organization requires to function effectively.
The path a purchase order takes from creation to closing, including everything in between, is referred to as the purchase order process.
It can be modified to include extra necessary steps such as quality checks, budget approval, contractual approval, and more, depending on the nature of a company (size, industry, human resources, organizational structure, the goods and services it is acquiring, and so on).
Steps involved in a Purchase Order Process
Creation of a PO
When an organization (the buyer) agrees to purchase a product or service, it prepares a purchase order that outlines the product or service being bought, as well as pricing and payment arrangements.
Approval of a PO
A PO must be approved before it can be sent. The approval procedure for an organization will determine who inside it should approve a PO before it is transmitted to the supplier.
Modern businesses often make this process easier by demanding (and approving) purchase requisitions first. This method deletes the requirement for PO approval and streamlines the buying team’s process.
Sending of the PO to the vendor
The PO is issued to the vendor once it has been approved. This step may appear unnecessary for software businesses that buy online. POs nonetheless act as internal document that helps the accounting staff with reconciliation after the invoice is received.
While sending the PO to the vendor isn’t compulsory, it is still a smart thought to maintain it for internal use.
Vendor receiving the PO
Now the order is received by the vendor/seller. The purchase order becomes a legally binding contract after the seller confirms that it can fulfil the order.
E-procurement technologies help you to submit POs using an online procurement system, making it easy to track if the organization sent and received emails containing POs.
Receipt
The order is shipped, with the PO number attached to the packing list. The buyer will be able to identify which order has arrived as a result of this.
Invoicing
The seller also generates an invoice for the order, making sure to include the PO number.
Three-way matching
The organization employs 3-way matching to ensure that the PO number and order data (quantities and prices of products and services bought) on the Purchase Order, Invoice, and Packing Slip are all the same.
Payment
If everything checks out and the organization is pleased with the order, the invoice is approved and payment to the vendor is arranged (as per the agreed-upon payment terms).
Closure
The PO is marked as closed once all of the aforementioned processes have been performed.

Who issues a Purchase Order?
A purchase order must be created and issued by the buyer. The purchase order is usually issued by a procurement or purchasing department in larger corporations. In smaller businesses, the purchase order may be issued by the owner, operations manager, or financial manager.
It’s also worth noting that the duty of drafting and issuing a purchase order for a certain team might be assigned to a central purchaser. An office manager, for example, at a software firm, can create purchase orders.
In the end, how an organization chooses to set up its purchasing process determines who issues the purchase order.
Who authorises a Purchase Order?
Depending on the purchasing process in place, one or more persons can authorize purchase orders. Purchase order approvals are often structured around locations and departments in bigger firms with structured purchasing processes, with precise cost criteria attached.
For instance, if a software company’s digital marketing manager requests a new ad budget, the purchase order approval route may include a marketing director and a CFO (or another role in charge of the company budget).
In smaller businesses, the CFO or CEO may be the final approver for any expenditure, resulting in approval delays.
What is the Format of a Purchase Order?
Generally, a Purchase Order’s contents look like the following:
- Products or services being purchased
- Quantity of products/services purchased
- Specific brand names, SKUs, or model numbers
- Price per unit
- Date of delivery
- Delivery location
- Company billing address
- Agreed payment terms
Depending on an organization’s procurement and purchasing operations, these things may be mandatory prerequisites or optional. Purchase orders can also be adjusted to meet a company’s specific needs, so this list isn’t absolute.
You may add account codes to requisitions using e-procurement software. By including this information, you will be able to speed up the reconciliation process and send data to your accounting system.

Example Of Purchase Order Format
Your purchase order doesn’t have to look exactly like this. But it should include these elements.
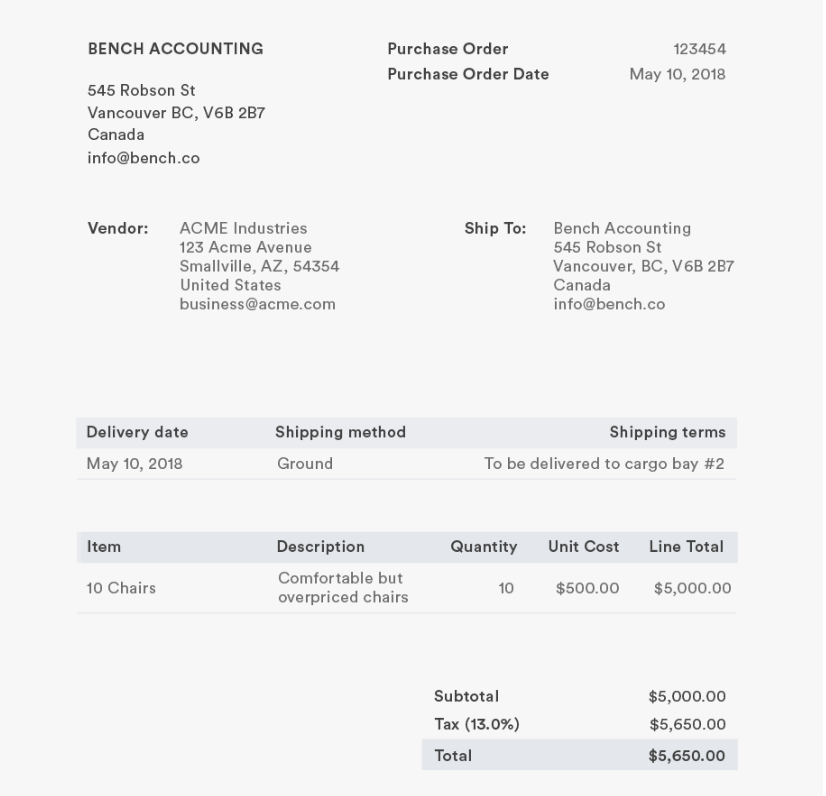
The elements included in this example are:
- PO number
- Purchase order date
- Vendor name and billing address
- Buyer name and shipping address
- Additional contact information, such as phone numbers and email addresses
- Delivery date
- Shipping method
- Shipping Terms
- Item name
- The item description and technical information
- Item Quantity
- Item unit cost
- Line total
- Taxes
- Total price
- Payment terms
Purchase orders are standardized across the entire company and contain, at the very least, information about: the purchaser and vendor (names, addresses), the order itself (product description, technical specs, price, quantity), and payment terms (due date and form of payment, eg. bank transfer, credit card).
These days, most companies use an electronic purchase order system, typically managed with accounting software.
What is the Difference Between a Purchase Order and an Invoice?
If you’re unfamiliar with POs, you may be curious about how they are different from invoices. To begin with, these documents are created by several members of the team.
The PO is prepared by the buyer and sent to the vendor. As a result, the vendor accepts the PO and provides an invoice to the buyer.
It is not uncommon for the PO and the invoice to include the same information. The invoice usually includes a reference to the PO number as well as an invoice number to ensure that both documents are consistent and match one another.
| PURCHASE ORDER | INVOICE | |
| Who creates it? | Buyers are in charge of generating POs | Invoices are the responsibility of the vendors |
| When is it sent? | Prior to purchase, approve and give to the vendor, or keep for internal records. | Once payment has been accepted, generate and send an invoice. |
| What does it include? | Details about what is being bought, SKUs, model numbers and brand names, Price, Date of delivery, The location of the delivery, Address for billing terms of payment. | PO number, Invoice number, Listed compartmentalization of the order with the cost |

What are the advantages and Disadvantages of using a PO?
Let us now know about both advantages and disadvantages of a purchase order.
Advantages of using a PO
POs are significant because they may assist businesses in the following ways:
- Avoiding orders that are duplicated
- Avoiding getting taken by surprise by unexpected invoices
- Keeping track of incoming orders
- Taking advantage of unexpected price hikes
- Increasing the accuracy of a company’s inventory and finances
- Obeying all auditing standards
- Smarter budgeting: procurement teams can only buy using finances that have been approved
- POs help to plan a delivery for whenever the buyer wants it, which helps to improve (and even speed up) delivery times.
- Maintaining clear communication with vendors.
- Acts as a legally binding document
Disadvantages of using a PO
- POs add extra paperwork to the process, which may be inconvenient for transactions that are small or not as big and are therefore time-consuming for small teams.
- Credit cards can be used in place of POs to aid with record keeping and documentation of transactions, even though they are not a formal contract between the vendor and the supplier. (Keep in mind that if an organization uses credit cards for purchases, POs can help the accounting staff with credit card reconciliation).
Should you use Purchase Orders at your company?
Utilizing purchase order forms can support an organization in transforming from a reactive to a proactive spending culture. So, should your company be using purchase orders or not?
To answer this question and develop a purchasing strategy that works for a company, business owners should take a step back and look at how their company generally handles purchasing.
POs make business owners cognizant of their company’s spending. They assist team members in making quick purchases and streamlining the purchasing process. They also facilitate accounting teams in reconciling expenditures.
Things company owners should analyse before implementing Purchase Orders
These are the things that all business owners must analyse before implementing PO.
Purchase Requisitions
If your company doesn’t employ purchase orders, it is also probable that you are not keeping track of the requests your employees make when they want to buy something. Most businesses simply ask their employees to email their requests to a manager, who will subsequently make the appropriate purchases.
If your firm is small and team spending does not exceed your budget, an informal purchase approval procedure is unlikely to be an issue.
However, when your firm expands and new teams begin to purchase products and services, you will need to tighten up your spending rules. Purchase requisitions will prove of assistance in this situation.
Requisitions are purchase order requests made by members of your team for supplies or goods they require to complete their tasks. When a team member makes a request to their manager or directly to the procurement team, the request is then approved or denied.
You may avoid wasteful and needless expenditures and bring your company’s spending under control by formalizing the process of requesting a purchase.
Keep in mind that incorporating purchase requisitions into the purchasing process adds an additional step to the process. So, before moving further, assess whether the benefits exceed the disadvantages.
Budgets
If bringing your business’s budgets under control is a concern of top priority, you should know that incorporating PO requests brings two key advantages: the ability to monitor a budget for team spending and the ability to take advantage of volume discounts on large purchases.
You’ll be able to calculate an average monthly spend and watch what your teams are buying as soon as team members start drafting purchase requisitions. This means you may start studying how they use goods and see where you can save money.
The person in charge of the budget will be an approver. If a team exceeds the set budget, the approver may not approve all purchase requisitions that are not urgent.
Volume Discounts
Could there be a possibility that buying in bulk will bring you higher vendor discounts? If that is the case, POs and purchase requisitions will most certainly come in handy.
The approver can simply spot purchasing patterns once your teams start submitting purchase requisitions. The approver can then place large orders and negotiate vendor discounts.
Because teams may add commonly requested goods to a catalogue from the best source at the best price if the requests are digital, it can dramatically save processing time.
Purchase Orders
Setting up a purchase order process is likely as easy as contacting suppliers and notifying them that you would be submitting a PO before providing payment for items from now on. This will most likely delight the supplier because it will greatly benefit both parties.
When an authorized request is ready for purchase, the purchaser will fill out a PO form and submit it to the vendor.
A seller will convey any problems or difficulties with the transaction in a transparent and concise manner. They will deliver the goods and provide an invoice after they have received payment.
When you employ e-procurement software, introducing a PO process is significantly easier for you, your departments, and your vendors.
Also Read: Credit Management Guide for SMBs – things you must know

Maximize Your Online Business Potential for just ₹79/month on Lio. Annual plans start at just ₹799.
How can Lio help?
Lio helps companies and business owners in automating their Purchase Order Process. The automation of the whole purchase order process is known as purchase order automation. The primary benefit of Purchase Order Automation is the time and effort savings.
The automation platform facilitates team members in big organizations to forward purchase requests to the team leader for review and approval.
The PO would then be generated automatically, removing the need for paperwork, repetition of data entry at various levels of approval, and other issues such as:
- Inefficiency and lack of accountability
- Inadequate process control
- Threats to privacy and security
Automation with Lio guarantees that rules and controls are followed, while also increasing your team’s process efficiency and reducing human error. Furthermore, it gives a complete audit trail, which eliminates the effort of looking for misplaced paper files.
Flexibility, control, and insight into the processes come with a simplified process and cost and time savings. Furthermore, in an automated AP department, an automated purchase platform allows for smooth invoice matching.
Not downloaded the Lio App yet? Here is how you can start with Lio App.
Step 1: Select the Language you want to work on. Lio for Android

Step 2: Create your account using your Phone Number or Email Id.
Verify the OTP and you are good to go.
Step 3: Select a template in which you want to add your data.

Add your Data with our Free Cloud Storage.
Step 4: All Done? Share and Collaborate with your contacts.

Conclusion
Many businesses avoid issuing purchase orders because they don’t want to engage in more paperwork or slow down their ongoing operations.
However, unless your company is small and only makes a few purchases from a few vendors each month, you’re probably not taking advantage of the many perks that a purchase order system has to offer to your organization.
Purchase orders provide vendors with clear legal regulations and purchase instructions. They provide an audit trail for an organization. When things go wrong in the financial world, finance executives can resort to this document.
I hope this article has helped you in understanding purchase orders and their format.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
What is the difference between a purchase order and a sales order?
A purchase order is a document that a buyer generates and delivers to a seller for signature, whereas a sales order is a document that a seller creates once a buyer’s purchase order has been approved.
What are the Various Purchase Order Types?
Different types of Various Purchase Orders are-
Standard PO
Contract PO
Planned PO
Blanket PO
What to include in a Purchase Order?
Product details
Quantities
Price
Date of the purchase order.
Payment terms.
Business information
Shipping address.
Purchase order number
Why should I implement a Purchase Order Process for my Business?
Purchase Orders guarantee that an order’s specifics are not misplaced, payments are not missed, and the same order is not repeated. They save time and create a paper trail.
Purchase Orders that are properly logged provide a visible history of what things were purchased by your company, who purchased them and when, who are the typical vendors, and how much spending money is available at any given moment.
Purchase Orders vs Invoice
A Purchase Order:
PO is established by the buyer before making a purchase
contains information on the items or services to be purchased
includes a suggested payment schedule.
An Invoice:
Invoice is raised after the sale by the seller (purchase)
verifies the supplied products/services with an itemized pricing list
Specifies a payment schedule with dates
Can we say that a Purchase Order is a Contract?
A purchase order is a legally enforceable contract once it is accepted by a seller.
Vendors ‘accept’ a purchase order by informing the buyer that they are capable of filling it. Vendors can “refuse” a purchase order by informing the buyer that they are unable to fulfil it.
If the process includes a Request for Quotation (RFQ), the vendor can simply refuse the RFQ to signal that they are unable to fulfil the order.






6 Comments
Great post. Learned so much about the purchase order, its working, issues, format, advantages, and disadvantages. Thank you for this well-researched article.
Hello Ishaan,
Thankyou for the kind words.
I am glad that you found this article informative.
Wow! Lio has purchase order templates too! Lio is gonna help a lot in many industries.
Hello Mehak,
So glad you found this essay to be enlightening.
I appreciate your kind words. Check out the Lio app and share your thoughts with us.
I happened to read this article’s overview of purchase orders and purchase requisitions. What is the main distinction between the two?
Hello Kaustubh,
A purchase requisition is a document that an employee uses to request purchases, whereas a purchase order is the department head’s approval of an order. The approval of the relevant department to purchase supplies from the vendor is indicated by the purchase order and the purchase requisition is used to inform the relevant department that materials are needed.