What is a bank reconciliation statement? A Step by step guide

A lot of users find themselves wondering what a bank reconciliation statement is and the world of the internet seems to puzzle them further. If you are one of them, worry not! We are providing you with a step-by-step guide on what a bank reconciliation statement is and other technicalities related to it.
Understanding What A Bank Reconciliation Statement Is
Business bank accounts might have thousands of transactions every month. An organization’s book balance for its checking account seldom matches the amount that the bank records show for the business at any one point due to the high number of ongoing transactions.
These temporal disparities are often driven by the fact that certain transactions are known to the organization before they are known to the bank, and some transactions are known to the bank before they are known to the organization.
When such a high rate of transactions involves a bank account, an internal system of auditing is strongly recommended to ensure that all cash transactions are accurately documented in the bank account as well as on the business’s ledger.
The bank reconciliation is an internal accounts report that analyzes and records any inconsistencies between a company’s checking account balance as shown by the bank’s records (bank balance) and its accounting records (company balance).
A bank reconciliation statement tries to balance an entity’s bank account with its financial records by summarising banking and commercial activities.
The statement details the deposits, withdrawals, and other transactions that have transpired in a bank account over a given time period. A bank reconciliation statement is a valuable financial internal control tool for detecting and preventing fraud.
Bank Reconciliation Statement (BRS): Step by Step Guide
The bank will send you a bank statement once a month, generally somewhere towards the end of the month. The statement details the cash as well as other deposits processed into the business’s checking account. Bank costs, such as account servicing fees, are also included in the statement.
Take the following steps to reconcile a bank statement once you have received it:
Select an appropriate Reconciliation method
The method you pick to make a bank reconciliation is determined by how you handle and manage your money. Accounting software or mobile applications are used by some people to manage monetary operations and reconcile banking activity.
Some keep track of their written cheques and other transactions in a paper chequebook that they balance once a month. You may also keep records of your transactions in a simple notepad or spreadsheet.
Whatever approach you choose, it is critical to keep detailed records of all transactions in order to correctly balance your bank account.
Compare your deposit amounts
Compare your current bank statement to your personal transaction history. To begin, double-check that all of the deposits shown on your bank statement have been entered into your personal file. If not, make a note of the missed deposits as well as your overall account balance.
Check your bank statement to determine if all of the deposits indicated in your records are present. Analyze why a deposit went missing if it was not received by the bank.
It is possible that the deposit showed up after the deadline for the monthly statement issue. You may receive email or SMS alerts for successful deposits into your account, based on how you want to receive notifications from your bank.
Check your history for any missed notifications. Call your bank to look into the matter further and determine the source of the problem. Once you have figured it out, be sure to update your accounts to match the deposits.
Accordingly, adjust bank statements
Make the necessary adjustments to the bank statements’ balances to reflect the updated amount. You should include deposits in transit, subtract outstanding checks, and add/deduct bank mistakes to do this.
Amounts received and documented by the organization but not yet registered by the bank are referred to as deposits in transit.
They need to be included in the bank statement. Outstanding cheques are cheques that have been made and entered into the business’s cash account but have yet to clear the bank account.
They must be subtracted from the bank account balance. This frequently occurs when cheques are issued in the final days of the month.
Make required changes in the cash amount
The cash balance in the corporate account must then be updated. This can be done by either adding interest to the cash balances in the business account or subtracting monthly charges and overdraft fees. Businesses must account for bank fees, NSF checks, and accounting inaccuracies in order to do this.
- Bank costs are fees and service charges levied by the bank for managing the checking account operations of the business. This might involve monthly fees or fees incurred as a result of an account overdraft. They should be taken out of your bank account. Any interest generated on your bank account balance must be transferred to the cash account.
- A cheque that has been returned by the bank owing to insufficient money in the issuer’s bank accounts is known as an NSF cheque. It indicates that the amount mentioned on the cheque is greater than what is available in the account and has not yet been put into your bank account. Therefore, it must be debited from your cash account records.
- When there are mistakes in the cash account, a wrong amount is recorded or an amount is missed from the records. The cash account in the books will increase or decrease when the error is rectified.
Compare the balances
The revised amounts should be the same after updating the balances according to the bank and the records. If they are still not similar, you will have to go through the reconciliation procedure again.
Businesses must produce journal entries for the changes to the balance per book once the balances are equal.
Example of Bank Reconciliation Statement Procedure
Consider the following scenario for XYZ Company, a small business.
- After all, posting is done, the book balance at the end of July 31 is $32,760, and the bank statement amount is $77,040.
- There are two outstanding checks: 5523 for $9,620 and 6547 for $10,000.
- The $2,000 check 5386 is properly withdrawn from the bank account, however, it is documented on the accounting records as $1,760. This was in the form of a dues payment. The transaction’s consequences resulted in a $320 mistake, which must be removed from the company’s book balance.
- The $34,300 deposit was submitted to the bank after hours on the night of July 31. As an outcome, the deposit appears on the financial records rather than the bank statement.
- A mistake is detected when the bank statement is examined. A cheque for $240 is taken from XYZ’s account, which should have been withdrawn from the account of some other bank customer.
- A remark on the bank statement states that the bank received $60,000 in charges (payments) and $1,800 in interest from the credit card company. This transaction appears on the bank statement but not in the financial records of the business.
- The bank informed XYZ that a $2,200 cheque from client ‘B’ had been returned unpaid owing to insufficient money in B’s account. This cheque return appears on the bank statement but does not appear in XYZ’s records.
- The bank service fee for the month is $80. They have not been mentioned on XYZ’s records.
A bank reconciliation statement should be prepared after recording the journal entries for the company’s book adjustments to reflect any changes in cash balances for each month. Auditors utilize this statement to undertake year-end audits on the business.
Why do businesses prepare a bank reconciliation statement?
You may be curious as to why bank transactions recorded in the books of accounts do not match the bank statement, given the description of a bank reconciliation statement. There are several causes for this, and some of the more common ones are given below:
- Outstanding Cheque: a cheque that was issued and deducted from the organisation’s financial records but not received by the recipient, resulting in the money not being withdrawn from the bank account.
- Deposit in transit: It is a deposit made by a company and documented on its records but not yet registered by the bank.
- Deductions for a bank service charge: Banks frequently impose monthly fees for account maintenance. Set maintenance costs, per-check fees, or a penalty for a check made for an amount larger than the checking account balance, known as a nonsufficient funds (NSF) cheque, are examples. The bank deducts these costs from the account, but they are not recorded in the financial records.
- Errors caused by the customer or the bank: for example, the client may inaccurately register a check in its accounts for a higher or smaller amount than what was issued. A cheque with an inaccurate value or in the incorrect client’s checking account may also be reported by the bank.
- Additional funds collected by the bank: Interest and money collected by the bank for the customer are deposited to the bank account as they are received, but they are not reflected on the financial records. These additions may also include funds collected for the account holder by the bank.
The closing bank amount in your accounting records and the real bank balance as per bank will not tally for the reasons stated above. This implies that the bank balance you think you have in your account is not the one that is actually available. Making decisions based on the balance in the account can place you in an awkward predicament.
Bank reconciliation statements are created to avert such problems. This statement simply compares the bank transactions in the account reports of the companies with the bank statement, ensuring that the bank balance in the books of accounts is always accurate.
How often should you reconcile your statements?
Reconciliation operations can be performed on a daily, weekly, fortnightly, or monthly basis, depending on the number and value of bank transactions. Reconciliation processes are carried out daily if the number or value of transactions is larger, to reduce the chance of payment/cheque bounce.
In any case, bank reconciliation should be done on a regular basis, irrespective of the frequency. Despite the fact that some businesses still maintain their records by hand, accounting software is available to make the process easier and more efficient. The majority of these tools combine the company’s bank accounts, allowing all data and records to be accessed at one spot.
It is essential to keep updated. The more often you reconcile your bank statements, the less difficult it becomes each time.
If you haven’t reconciled your bank statements in six months, for example, you will need to review 6 months’ worth of items listed. The number of transactions and your level of patience will determine whether or not this is a wise option.
It is best to stick to a routine. Make a plan for how often you will reconcile, and stick to it. This will prevent your unreconciled bank statements from being an overwhelming and time-consuming process. It will also keep you in touch with your company’s financial flow.
Benefits of preparing Bank Reconciliation Statement
When cheques bounce or businesses start getting bothersome calls from creditors or suppliers for funds that have already been released, accounting mistakes may lead to situations that are more than simply humiliating.
Bank reconciliations help in the detection of fraud and the reduction of the risk of transactions resulting in fines and late fees. A company can benefit from BRS in a number of ways, including:
To get a true picture of your company
You want to understand that your books are accurate when you look at them. If your bank account, credit card statements, and accounting are all out of sync, you might find yourself spending funds you don’t have—or hoarding money you could be putting in your organization. This can also benefit you in identifying any bank service charges or interest income, as well as ensuring that your company’s cash balance is right.
To keep a record of your cash flow
Handling cash flow is an important aspect of running a business. You can identify the connection between when money enters your company and when it reaches your bank account by reconciling your bank statements, and arranging how you receive and spend that money properly.
Identifying mistakes
A bank reconciliation improves the process of detecting accounting errors that may often occur in all businesses. Computation blunders, lost payments and duplicate payments are examples of these errors.
Monitoring Interest and Fee
Banks may charge you interest, fees, or fines on your account. You can add or deduct such sums in your records using monthly bank reconciliation.
Preventing Fraud
Reconciling your bank statements will not prevent fraud, but it will alert you to the fact that it has occurred.
You could, for example, pay a supplier through cheque, but they may manipulate it and increase the amount to be withdrawn before cashing it. You will not know until your account gets charged by the bank. When you reconcile your bank statement, the disparity will show up.
Alternatively, you and your business partner might have a joint account. They may take more than the record on the books when they withdraw money from your account to pay for a business cost. When you reconcile your bank statement, you will discover this.
While you may be unable to keep your employees from stealing your money once, you can stop it from happening again. You may use a bank reconciliation statement to discover and recognize fraudulent activities. To prevent your accounting staff from faking your records and reconciliations, you should hire an independent professional to file the reconciliations.
Receivables Tracking
BRS enables you to double-check all of your invoices, helping you prevent unpleasant situations and finding entries for receipts that you didn’t deposit.
When you conclude a project assigned by a customer and they tell you that they have dispatched or submitted the cheque, you may debit your cash account if you utilize the accrual method of accounting. Then, a month later, you complete your bank reconciliation and discover that the cheque never arrived, and the money isn’t in your records, even though your bookkeeping would show that you got paid.
Bank reconciliations act as a safety net to ensure that your receivables never spiral out of hand. And if there is a continuous difference in accounts receivable between your balance sheet and your bank, then know you have got a bigger problem to solve.
Who makes bank reconciliation?
If you manage your own accounting, you need to plan focus on reconciling your bank accounts on a regular basis (more on that below). If you hire an accountant or use an online accounting service, they will take care of it.
If you adopt the accrual method of accounting, you simply have to reconcile bank statements. This is to ensure that all of the uncleared bank transactions you documented were completed.
If you apply cash basis accounting, on the other hand, you document every transaction at the same moment the bank does; your financial statement and bank statement should be comparable.
There will be someone monitoring to make sure every figure adds up and the records reflect facts at large companies employing full-time bookkeepers. This is normally the owner’s responsibility in a small business (or a bookkeeper, if you hire one).
What is a ‘general entry’ in bank reconciliation statements?
If there are revisions to the balance as per both cash books and passbooks, general entries are necessary for a Bank Reconciliation statement. Items showing on the bank statement which have not been entered in the company’s general ledger accounts have resulted in these adjustments.
The following are examples of common modifications or general entries to the balance per book:
- Fees for maintaining the account, the penalty for returned checks, processing wire transfers, check to print, and other examples of bank fees or service costs.
- Interest earned in the bank
- Payments on a loan
- Supplier and other electronic costs and remittances
- Checks from customers that were deposited but are now being reimbursed owing to a lack of sufficient balance
How to file for a Bank Reconciliation Statement?
In order to make adjustments to the financial records, rectify any inconsistencies, and identify fraudulent activities, you would compare the cash balances on the balance sheet to the matching amount on your bank statement. This way you would find the differences between the two and do a bank reconciliation.
The account balance recorded by the bank is matched to the general ledger of an organization to reconcile a bank statement.
A cash book is used by businesses to keep track of both bank and cash transactions. The available cash is shown in the cash book’s cash column, while the cash at the bank is shown in the bank column.
Similarly, every consumer has an account with a bank. Deposits are documented on the credit side of the bank books, while withdrawals are documented on the debit side. Customers receive their account statements every month or at regular intervals from the bank.
These balances might not always match. The business must determine the cause of the discrepancy and reconcile whatever differences there are. This is done to make sure that all items have been accounted for and that the final balances are accurate.
A bank reconciliation statement, often known as a reconciliation statement, is generated to do this.
Guidelines for preparing a Reconciliation Statement
- The heading is usually written as follows: Bank Reconciliation Statement as on – particular date.
- ‘Balance, as shown by the Cashbook’ or ‘Balance as shown by the Passbook’, should be the place where you start. In the cashbook, the ordinary bank balance is debit, whereas, in the passbook, it is credit.
In the cashbook, however, the overdraft balance is a credit balance, but in the passbook, it is a debit balance.
- By reviewing the entries made in these two books throughout the relevant period, the various explanations for the discrepancy between the two balances should be identified.
- The impact of a specific reason on balance presented in the other book should be examined in terms of increase or decrease in the balance.
- If the outcome is an increase in the other book’s balance, the value of the increase should be added to the starting balance. If the outcome is a decrease in the passbook amount, the value of the decrease should be subtracted from the cashbook balance. Thus, the balance reflected in the other book will be obtained by adjusting all ‘increase’ and ‘decrease’ items to the starting balance. When the balances reported in the cashbook and passbook accord with the Bank Reconciliation Statement, it is assumed that the entries made in these two books are just different, not incorrect.
Types of Bank Reconciliation Statements
Bank reconciliation, also known as bank statement reconciliation, is the way of evaluating the bank balance in a company’s account books with the bank’s statement of account. Each transaction in the bank statement is matched with the company’s internal data (usually the cash account) to ensure that the two records are the same.
To avoid missed payments and calculation errors, bank reconciliation should be done on a regular basis. It will also facilitate the detection of theft and fraud, as well as the tracking of account payments and receivables.
There are many types of reconciliation statements. They have been listed below:
- Vendor Reconciliation: A vendor reconciliation statement is produced to verify that the accounting entries recorded in the vendor’s books correspond to the accounting entries recorded in the company’s books.
- Customer Reconciliation: A vendor reconciliation statement is comparable to a customer reconciliation statement. It is generated to check if the customer’s books and the business’s books are in sync. The majority of corporate clients prioritise reconciliation above vendor reconciliation. It is so because payment is receivable from consumers, and it is generally a good idea to reconcile so that payments aren’t delayed due to errors in accounting records.
- Credit card reconciliation: The process of reconciling credit cards and bank accounts is extremely similar. A company matches credit card receipts to the state of a credit card provided by a financial institution in this situation. This enables financial organisations in ensuring that the amount invoiced on the credit card statement corresponds to the actual payments. If a credit card issuer makes a mistake, it should be notified and fixed as soon as possible.
- Cash Reconciliation: This is the method of ensuring that the amount of cash in the cash register corresponds to the amount of money on hand at the end of the business day. Each of the above-mentioned reconciliation kinds has its own workflow. There are various reconciliation solutions available, each of which is highly tailored to fit the specific requirements. There are also next-generation reconciliation systems that can easily and accurately reconcile any account.
- Inter-Company Reconciliation: Integrated accounting records are required for group corporations (holdings, subsidiaries, and so on). These records are needed to close inter-company transactions involving a sale from the parent company to a subsidiary. As a result, it is important that their accounting records are always in alignment, and that they be reconciled on a regular basis before the consolidation process is finished.
- Business-specific Reconciliation: In addition to the variety of reconciliations listed above, each company must generate extra reconciliations depending on its individual requirements. An excellent example is the Cost of Goods Reconciliation. This reconciliation statement should be prepared by any company with inventory to match the balance on the cost of sales of products determined using two approaches.
Should companies use accounting software for bank reconciliation? Why?
Applying the manual and traditional approach of bank reconciliation, comparing the two statements with a big list of transactions is stressful and prone to blunders.
The one and only solution to avoid this are to use accounting software to ‘automate’ the bank reconciliation procedure. In day-to-day operations, it reduces the workload. More critically, you gain precise, near-real-time bank balance information in your account books.
The following are some of the advantages of adopting accounting software to automate the bank reconciliation procedure.
- Simple to reconcile: Using accounting software can assist you in automatically preparing a bank reconciliation statement and reconciling with less effort.
- Reduces the burden: Whether there are 50 or 500 transactions to reconcile, the work and time spent are the same. Because it is automatically reconciled, you can save a huge amount of time and energy in reconciling banking activities.
- Easy to spot unaccounted transactions: Learn about new (unaccounted) transactions, such as bank fees or bank interests, and simply account for and reconcile them.
Reconciliation Tips for a Smooth Process
Based on the number of monthly transactions you perform, reconciling your bank accounts is a pretty simple and swift process.
It’s a key component of the financial planning puzzle for ensuring consistency and supporting you in attaining your financial objectives. Other things to think about while you prepare to reconcile your bank accounts are:
- Consider adopting accounting software: Accounting software may make the process of documenting transactions simpler. Many mainstream accounting software applications allow you to automatically import data by linking your bank accounts, other financial accounts, and card accounts.
- Use a budgeting tool to keep track of your spending: Budgeting applications help you in setting and managing monthly budgets, and most include tools for tracking expenditure across connected accounts. Using a budgeting tool allows you to view a snapshot of your spending and money throughout the period of a month, allowing you to see any problems early on.
- Find a system: It is possible that what works for someone else probably wouldn’t work for you. Adopt a method that works best for you and your situation for keeping track of your financial transactions. Try out a few different approaches before settling on the one that enables you to retain the most accurate data.
Common Problems with reconciling bank statements
Bank reconciliations aren’t always easy. Generally, there is no quick account reconciliation since at least some research work is required to identify where the inconsistencies are coming from and which financial entries must be recorded to keep records synchronized.
In other circumstances, reconciliation concerns may reveal the necessity for alternate payment terms, banking choices, or withdrawal protections in a corporate relationship.
Simple problems originating from money movement delays to more complicated challenges such as fraudulent activities are among the most prevalent bank reconciliation concerns.
- Cash-In-Transit: Since cash does not flow immediately, in-transit checks and deposits might cause the bank’s reconciliation to fail. A company has documented this activity of money when it receives a check, electronic payment, wire transfer, ACH transfer, or cash deposit, but the bank has not yet obtained the funds. This is particularly troublesome with higher-volume accounts, where a constant flow of cash is going in and out of the account at the same time. The financial statement of a business will not mirror its bank statement record if the money gap is a recording period.
- Outstanding Cheques: When cheques are written but not cashed or deposited on time, bank reconciliation problems can develop. Booking an entry to transfer this check balance over to the following month will integrate accounts for the ongoing reporting period whilst still enabling the company to maintain track of check obligations.
A reconciliation issue might also be caused by unpaid cheques that are never submitted for payment. Additional actions should be made to settle the dispute once a reasonable time for depositing the cheque has elapsed.
- Errors: Errors in recording might force a cheque or deposit value to be entered inaccurately, thwarting a reconciliation attempt abruptly. While these errors are significantly more prevalent on the business side than on the banking side, either organisation can make them. Having the exact numbers recorded for each transaction promotes seamless bank consistency and reduces the need for later adjustments.
When a check or deposit is misplaced, an error might arise. This is, once again, more frequent in the commercial world. With the advent of automatic bank reconciliation tools in accounting system apps, it just takes one accidental click of a button to cause a transaction to go awry.
- Bank fees: Bank fees must also be accounted for after being responsible for the movement of money. Overdraft costs and Non-Sufficient Funds (NSF) check fees, for example, will toss a bank reconciliation away if they aren’t factored in. Due to poor cash flow management, these costs should ideally be minimised with frequent bank reconciliation operations.
For firms with significant bank charges, choosing a bank with a more liberal fee schedule or stronger overdraft protection should be considered.
- Unauthorised withdrawals: Fraud is a severe problem that many companies would rather sidestep. Internally, by a member of the staff or partner who should not have access to the account, or externally, by a third party who has intentionally breached the account, fraud may ruin a company.

Maximize Your Online Business Potential for just ₹79/month on Lio. Annual plans start at just ₹799.
How Can Lio Help?
Lio is a mobile integrated app that helps in maintaining the records of the activities as well as used for storage of other personal data and keeps it safe and secured so that the users know that their data will not get corrupted from any outer source. The app helps in categorizing, making folders, and storing data of various activities.
Not downloaded the Lio App yet? Here is how you can start with Lio App.
Step 1: Select the Language you want to work on. Lio for Android

Step 2: Create your account using your Phone Number or Email Id.
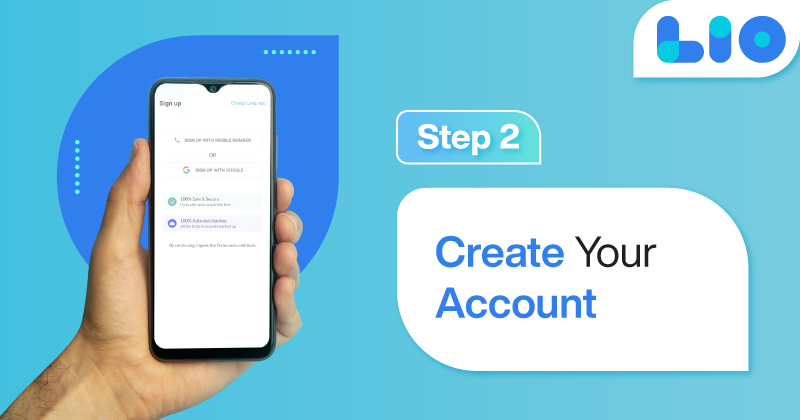
Verify the OTP and you are good to go.
Step 3: Select a template in which you want to add your data.

Add your Data with our Free Cloud Storage.
Step 4: All Done? Share and Collaborate with your contacts.

Conclusion
I hope by now you have understood that bank reconciliations are done by businesses across industries to assure the authenticity of their accounting records.
They can bring a sense of peace and order to some business owners. Any faults or adjustments which need to be done can be handled quickly by matching internal documents with external statements to finalize accounting close.
Bank reconciliation does not have to be a time-consuming and error-prone operation thanks to technological advancements.
The different sorts of financial reconciliations, from bank reconciliations to balance sheet reconciliations, are not going anywhere any time soon. Certainly, as more data and transactions are carried out online, the requirement for precise and genuine updates has evolved.
To get around bank reconciliation issues, you can use automation tools to perform the activity for your company whenever you want. So what are you waiting for? Kickstart your online tuition business by downloading Lio now.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
What is a bank statement?
A bank statement is a statement made by a bank that consists of the complete information of its depositor.
What are the primary advantages of creating a bank reconciliation statement?
The major advantage of generating a bank reconciliation statement is that it may be used to rectify any errors in the transactions recorded in the cash book and bank statement.
Why is it necessary to have a bank statement while producing a bank reconciliation statement?
The bank statement provides a lot of important financial data that is not included in the cash book and is useful for generating the bank reconciliation statement.
Is preparing a bank reconciliation statement compulsory?
The preparation of a bank reconciliation statement is not mandatory.
What information may be gathered from a bank reconciliation statement?
The bank reconciliation statement contains the following information:
– Bank account balance
– The amount of a dishonoured cheque.
– Interest on the whole deposit
– The total sum of charges
What is the distinction between a bank reconciliation account and a ledger account?
The main difference is evident in the separate columns for debit and credit. Since bank reconciliation statements do not have debit and credit sides like a ledger, they are not the same as a ledger account.
What is the definition of a bank overdraft?
The depositor’s excess withdrawal of money deposited in the bank is referred to as a bank overdraft.






6 Comments
Thank you for writing on this topic. I got to learn a lot. Could you suggest some accounting software for bank reconciliation?
Hello Meenal,
thankyou for the question.
Some of the best accounting software for bank reconciliation are AutoRek, BlackLine, Xero, OneStream, CashMatching, Cashbook, and ReconArt. Kindly research well and choose according to your requirements.
Could you help explain the distinction between a bank reconciliation and a bank statement?
Hello Aditi,
The bank prepares and provides the bank statement to its clients, but the customer must create the bank reconciliation in order to match the bank’s account movement and its balance on the company’s or client’s books.
Please list a few of the top reconciliation software as I am a bit baffled.
Hello Ronson,
Blackline, Redwood, Xero, Adra Accounts, and Traverse Distribution are some of the top reconciliation software. Please do your research and make responsible decisions.