What Is A Taxable Event Under GST?

What is a taxable event under GST? What is the scope of supply under the very law? If these questions have been baffling you, this article has got you covered!
Time to gear up and face the legal jargon!
What Is A Taxable Event?
A taxable event is one that occurs and results in tax liability. The occurrence of a taxable event is a crucial event in any law since the levy and collection of tax is dependent on it. Although the taxable event occurs at a specific time, the levy and collection of the tax may be postponed for administrative reasons.
The taxable event, or the moment in time when the tax will be imposed, is the basic pillar for the charging of tax under every taxation act.
Previously, each indirect tax had its own taxable event (for example, manufacture in the case of Excise Duty, provision of services in the case of Service Tax, sale of products in the case of VAT/CST, and so on). The provision of goods or services, or both, is a taxable event under the GST framework.
Article 366 (12A) of the Constitutional (101st Amendment) Act, 2016 defines “Goods and Services Tax” as any tax on supply of goods, or services or both, except for taxes on the supply of alcoholic liquor for human consumption
Components of A Taxable event
- All forms of supply of goods and services like sale, transfer, barter, exchange, licence, rental, lease or disposal.
- Made or agreed to be made for a consideration by a person
- In the course or furtherance in the business.
In order to fully grasp the concept of a taxable event under GST, it is important to understand supply under GST. The next section talks about supply under GST in great detail.
What Is A Supply Under GST?
Sale, transfer, exchange, barter, licensing, renting, lease, and disposal are all examples of supply. If a person engages in either of these transactions for a consideration in the course or advancement of their business, they will be included by the GST definition of supply.
Elements Of Supply
The supply consists of two essential elements:
- Supply done for a consideration
- Supply done in course of furtherance of business
Characteristics Of Supply
Supply of goods or services
If there is a transfer of title of commodities during a transaction, it is termed a supply of goods.
A provision of service occurs when a transfer of rights of commodities occurs without a transfer of title.
If you use transportation services, for example, the right to use the service is passed to you, but ownership remains with the transportation firm.
Supply should be taxable
A taxable or tax-exempt supply of goods or services exists. Goods and services that are subject to GST are known as taxable supplies.
Tax-exempt supplies are those that fall into one of the GST Act’s specified categories of goods or services.
Supply should be made by a taxable person
A taxable person is someone who is registered, or who is required to register, or who has voluntarily registered under the GST. Under GST, a supply between two non-taxable individuals is not deemed as a supply.
If a person provides products or services in many states or has several corporate verticals, they must register for each state or vertical separately. Each of these registered entities will be treated as a separate taxable entity.
Supply should be made within a taxable territory
Except for the state of Jammu & Kashmir, taxable territory refers to any region in India.
Supply should be made in exchange for consideration
Consideration is described as a barter of products or services or a monetary or in-kind payment for a supply. The government accepts an advance payment or deposit toward a supply as a kind of consideration.
The following actions shall be considered as a supply under the CGST Act, even if they are performed without consideration:
- When an enterprise disposes or transfers its assets permanently for which it has received input tax credits.
- For commercial purposes, a supply is made between separated or two related individuals.
- Products received by an agent on behalf of a client or goods supplied by an agent on behalf of a supplier.
- In case a taxable person gets services for commercial reasons from a related person or from his or her own business that’s not situated in India.
Supply should be made in the course of business or in order to enable a company to expand.
Only commercial transactions are subject to GST. As a result, a transaction must be performed for business objectives in order to be deemed a supply under GST. When supplies are provided for personal use, they are not considered supplies under GST.
While these six elements outline the definition of supply, there are a few exceptions to the requirement of supply be made for consideration and in the course of business.
Except in a few cases where a transaction is regarded to be a supply even without compensation, any transaction involving the supply of goods or services without consideration is not a supply.
Furthermore, whether or not in the conduct or furtherance of business, the import of services for consideration is recognized as supply.
Three Components Of Supply Under GST
Place, value, and time are three elements of a GST supply that are used to determine the tax due for that transaction.
- Place of Supply: This tell if you any transaction is an intra-state supply, inter-state supply, or a foreign trade, in turn, telling you the type of GST to apply.
- Value of Supply: This sections tell you the taxable value of a supply and, the final amount of the tax that one needs to pay.
- Time of Supply: It tells you when the applicable taxes and GST returns are due.
Types Of Supply Under GST
Supplies of goods and/or services are divided into two categories under the GST: taxable supplies and non-taxable supplies. Based on the nature of the supply, these are further categorized into several kinds.
Taxable Supplies
These are supplies of products and/or services that are subject to the GST. Refunds on tax paid during purchases are available to registered taxpayers.
- Regular taxable supplies
When you offer an item or service within India that has a GST rate of more than 0%, it is considered a regular taxable supply.
- Nil rated supplies
Nil-rated supplies are when you supply items that are subject to a 0% GST rate by default.
- Zero-rated supplies
When you make exports, supplies to an SEZ unit, or considered exports, the GST on the goods or services involved is zero, even though they would be subject to a GST rate higher than 0% if sold within India. These are referred to as zero-rated supplies.
Non Taxable Supplies
- Exempt Supplies
Even if they are subject to GST, the supply of exempt products or services is not subject to it. The registered taxpayer, however, cannot claim ITC on the inputs used to make such supply.
- Non-GST supplies
This refers to the sale of goods that are not covered by the GST act.
Composite Supply And Mixed Supply
There are a few products that are manufactured from two or more other items. Composite supply and mixed supply are two types of such supplies.
A supply that consists of two or more goods/services must be delivered together in accordance with common business procedures in that area.
To put it another way, these goods can’t be ordered separately. In the entire transaction, there is a principal supply and a secondary supply. The tax rate on the principal supply will apply to the entire supply in such instances.
A mixed supply is a supply that consists of two or more items or services that are not always required to be sold together and are independent of one another.
“It should not be a composite supply,” is the first criteria for mixed supply. The tax rate that is greater of the two supplies will be applied to the entire supply in such instances.

Maximize Your Online Business Potential for just ₹79/month on Lio. Annual plans start at just ₹799.
How Lio Can Help?
Lio is a mobile integrated app that helps in maintaining the records of the activities as well as used for storage of other personal data and keeps it safe and secured so that the users know that their data will not get corrupted from any outer source.
The app helps in categorizing, making folders, and storing data of various activities.
Not downloaded the Lio App yet? Here is how you can start with Lio App.
Step 1: Select the Language you want to work on. Lio for Android

Step 2: Create your account using your Phone Number or Email Id.
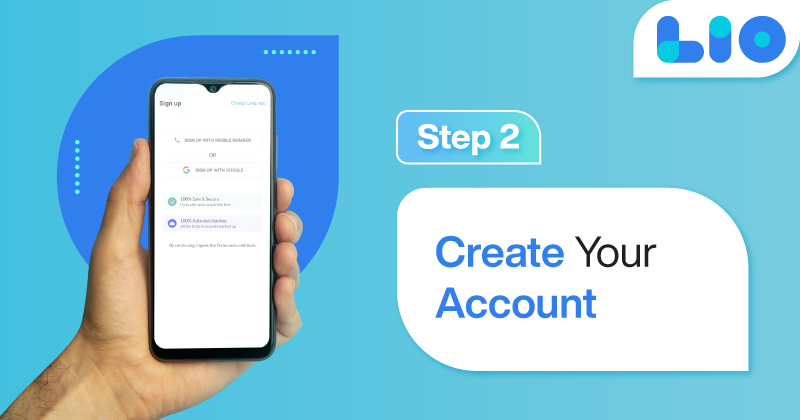
Verify the OTP and you are good to go.
Step 3: Select a template in which you want to add your data.

Add your Data with our Free Cloud Storage.
Step 4: All Done? Share and Collaborate with your contacts.

Conclusion
We are now familiar with taxable events, which are any occurrences that result in the liability to pay tax.
Manufacturing, sales, and the supply of services were all considered taxable events under earlier indirect tax legislation.
All of these events, however, are summed together in the GST definition of supply. Any provision of products and services, or both, in the course of a business, shall be considered a taxable event under GST.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
What is the scope of supply under GST?
The term supply has a broad definition, encompassing all types of supply of products or services, or both, including the sale, barter, transfer, exchange, license, lease, rental or disposal made or agreed to be made for a consideration in the course or advancement of business. It also involves service import.
The GST law also allows for the inclusion of some non-consideration transactions in the scope of supply.
What is a taxable supply?
A taxable supply is one that is subject to goods and services tax under the GST Act and includes both products and services.
What are the factors that make up a supply under the CGST/SGST Act?
The following elements must be met in order to be considered a ‘supply,’ namely:
– The activity entails the supply of goods, services, or both
– Unless otherwise specified, the supply is for a monetary consideration
– The supply is made in the course of or in promotion of a business
– The supply is taxable
– A taxable person makes the supply.
Are self-supplies subject to GST?
Even if there is no payment of consideration, inter-state self-supplies such as stock transfers, branch transfers, or consignment sales are taxed under the IGST.
In accordance with Section 22 of the CGST Act, every supplier is required to register under the GST law in the State or Union territory from where he makes a taxable supply of goods or services or both.
Intra-state self-supplies, on the other hand, are not taxed if they are not registered as a business vertical.






8 Comments
This subject has always puzzled me, but since reading your article, I feel much clearer about it. Thank you for explaining everything there is about taxable events to me.
Hello Raksha,
I really appreciate your warm comments.
I’m delighted you found this article intriguing.
Could you kindly explain the meaning of inward and outward supply in GST? Thanks in advance.
Hello Jithin,
When products or services are exchanged, the value of the goods and any applicable taxes move from the provider to the recipient while the goods themselves flow from supplier to recipient. The products or services that a supplier sells constitute his external supply, and the same is true of his internal supply to the recipient of the items.
I’m always confused of the differences between the terms tax and levy, so could you kindly clarify?
Hello Veena,
Taxes and tax levies are two ideas that are inextricably linked. The government imposes taxes on people and businesses, and these funds are utilized for a variety of things. Taxes are typically imposed on a business or an individual because they are typically not paid freely.
The government imposes a measure known as a tax levy when a taxpayer fails to honor his duty to pay tax. A tax levy enables a bank or other financial institution to seize a tax payer’s assets. If the taxpayer doesn’t make their required tax payments, the government will auction the confiscated property to recoup its losses.
I was inspired to learn more about this topic after reading your article. That’s when I came across the term “exempt supply.” If you don’t mind, could you please give a brief explanation?
Hello Taarish,
Exempt supply includes the non-taxable supply of any goods or services or both that attract a zero-rate of tax or are wholly exempt from tax under sections 11 or 6 of the Integrated Goods and Services Tax Act.